[1] The edited previous frame serves as condition for editing the next frame.
References
[1] Chai, Wenhao, et al. “StableVideo: Text-driven Consistency-aware Diffusion Video Editing.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09592 (2023).
[1] The edited previous frame serves as condition for editing the next frame.
[1] Chai, Wenhao, et al. “StableVideo: Text-driven Consistency-aware Diffusion Video Editing.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09592 (2023).
VM: guest OS -> BINS&LIBS -> App
Docker: BINS*LIBS -> App
https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/
sudo apt-get purge docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin docker-ce-rootless-extrassudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker, sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd 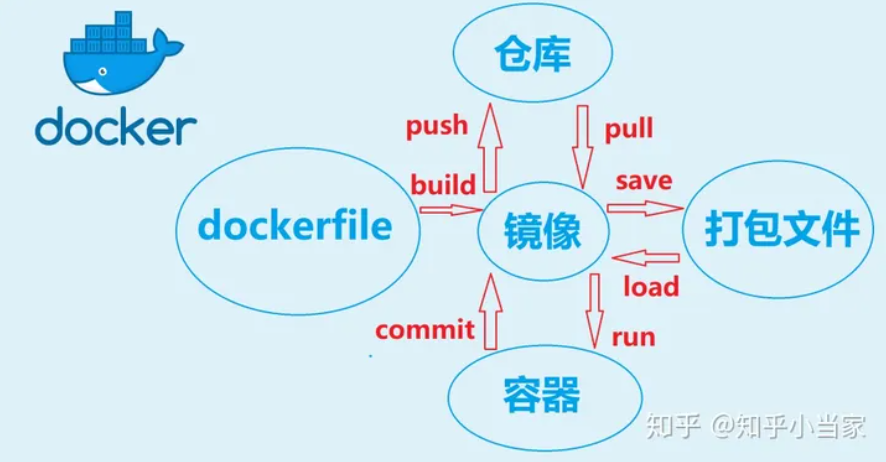
docker image pull $image_name:$version
docker image tag $image_name:version $registryIP:port/username/image_name:version
docker image push $registryIP:port/username/image_name:version
docker image build -t $image_name .
docker image ls
docker image rm $image_name
docker image save $image_name > $filename
docker load < $filename
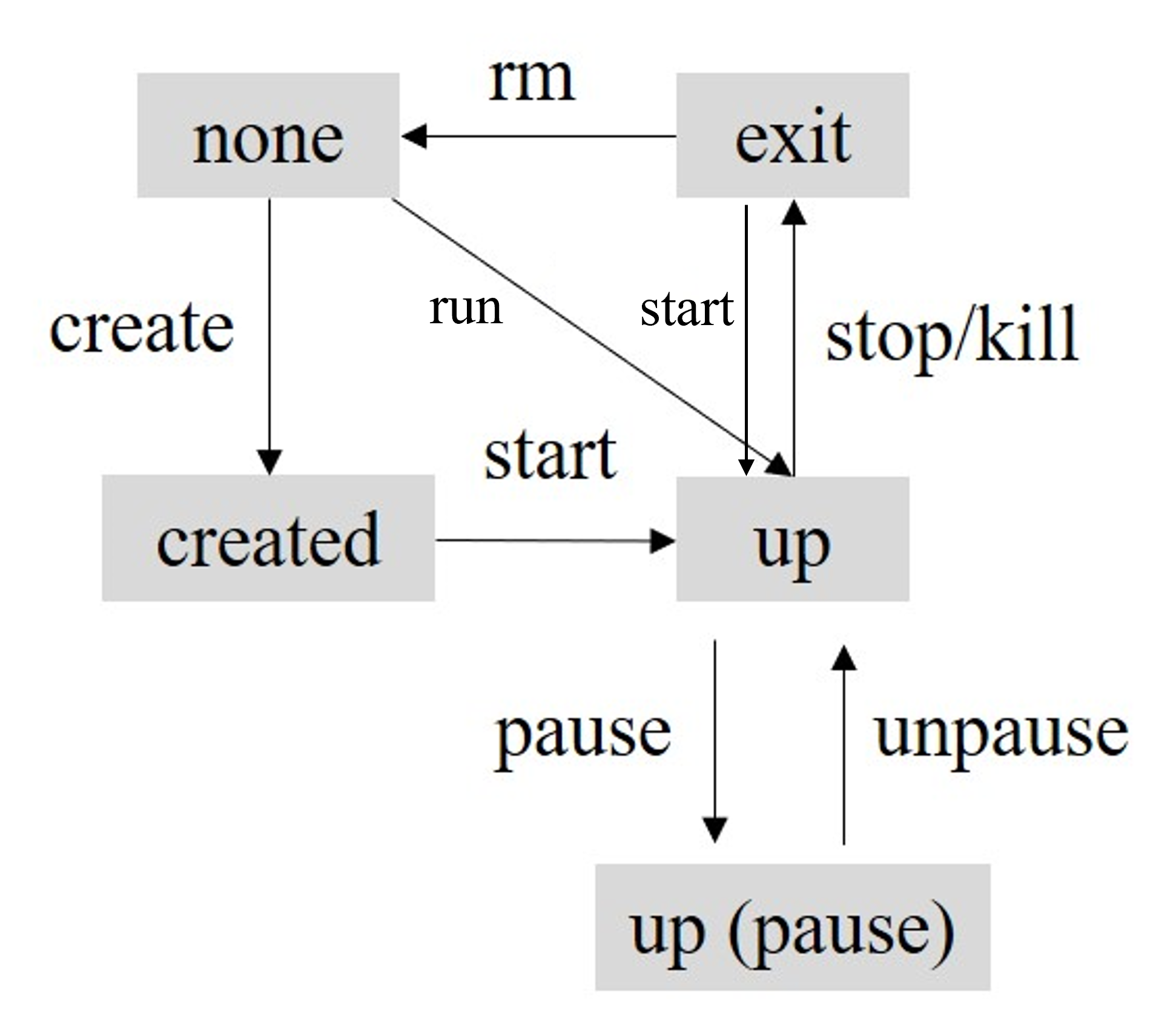
docker container create $image_name
docker container start $container_ID
docker container run $image_name # run is equal to create and start
docker container run -it $image_name /bin/bash
docker container ls, docker container ls --a
docker container pause $container_ID
docker container unpause $container_ID
docker container stop $container_ID
docker container kill $container_ID # the difference between stop and kill is that stop may do some clean-up before killing the container
docker container rm $container_ID
docker container prune # remove all the exit containers
docker container exec -it $containe_ID /bin/bash
docker container cp $container_ID:$file_path .
docker container commit $container_ID $image_name:$version
FROM python:3.7
WORKDIR ./docker_demo
ADD . .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
CMD ["python", "./src/main.py"]
Tutorial: [1]
Install nvidia-docker https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/container-toolkit/latest/install-guide.html
docker run --gpus all -it $image_name
SAM [1]
FastSAM [2]: first generate proposals and then select target proposals
High-quality SAM [3]
Semantic-SAM [4]: assign semantic labels
[1] Kirillov, Alexander, et al. “Segment anything.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.02643 (2023).
[2] Zhao, Xu, et al. “Fast Segment Anything.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.12156 (2023).
[3] Ke, Lei, et al. “Segment Anything in High Quality.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.01567 (2023).
[4] Li, Feng, et al. “Semantic-SAM: Segment and Recognize Anything at Any Granularity.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04767 (2023).
[1] Pan, Xingang, et al. “Drag Your GAN: Interactive Point-based Manipulation on the Generative Image Manifold.” SIGGRAPH (2023).
[2] Shi, Yujun, et al. “DragDiffusion: Harnessing Diffusion Models for Interactive Point-based Image Editing.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.14435 (2023).
[3] Mou, Chong, et al. “DragonDiffusion: Enabling Drag-style Manipulation on Diffusion Models.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.02421 (2023).
[4] Ling, Pengyang, et al. “FreeDrag: Point Tracking is Not You Need for Interactive Point-based Image Editing.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04684 (2023).
A survey on disentangled representation learning [1]
[1] Xin Wang, Hong Chen, Siao Tang, Zihao Wu, and Wenwu Zhu. “Disentangled Representation Learning.”
[2] Wu, Qiucheng, et al. “Uncovering the disentanglement capability in text-to-image diffusion models.” CVPR, 2023.
[3] Yang, Tao, et al. “DisDiff: Unsupervised Disentanglement of Diffusion Probabilistic Models.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.13721 (2023).
[4] Preechakul, Konpat, et al. “Diffusion autoencoders: Toward a meaningful and decodable representation.” CVPR, 2022.
[5] Kwon, Mingi, Jaeseok Jeong, and Youngjung Uh. “Diffusion models already have a semantic latent space.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.10960 (2022).
The target is separating foreground from background given some user annotation (e.g., trimask, scribble). The prevalent technique alpha matting is to solve $\mathbf{\alpha}$ (primary target), $\mathbf{F}$, $\mathbf{B}$ (subordinate target) in $\mathbf{I}=\mathbf{\alpha}\circ\mathbf{F}+(1-\mathbf{\alpha})\circ \mathbf{B}$ [1] [2] [3].
Alphamatting.com Dataset: 25 train images, 8 test images, each has 3 different trimaps: small, large, user. Input: image and trimap.
Composition-1k Dataset: 1000 images and 50 unique foregrounds.
Matting Human Dataset: 34427 images, annotation is not very accurate.
Dinstinctions-646: composed of 646 foreground images
Affinity-based [1]: pixel similarity metrics that rely on color similarity or spatial proximity.
Sampling-based [8]: the foreground/background color of unknown pixels can be obtained by sampling the foreground/background color of known pixels.
Learning-based
gradient loss [11] Laplacian loss [12]
Omnimatte [10]: segment objects and scene effects related to the objects (shadows, reflections, smoke)
unified interactive image matting: [13]
[1] Aksoy, Yagiz, Tunc Ozan Aydin, and Marc Pollefeys. “Designing effective inter-pixel information flow for natural image matting.” CVPR, 2017.
[2] Xu, Ning, et al. “Deep image matting.” CVPR, 2017.
[3] Zhu, Bingke, et al. “Fast deep matting for portrait animation on mobile phone.” ACM MM, 2017.
[4] Wang, Yu, et al. “Deep Propagation Based Image Matting.” IJCAI. 2018.
[5] Quan Chen, Tiezheng Ge, Yanyu Xu, Zhiqiang Zhang, Xinxin Yang, Kun Gai, “Semantic Human Matting.” ACM MM, 2018.
[6] Lutz, Sebastian, Konstantinos Amplianitis, and Aljosa Smolic. “AlphaGAN: Generative adversarial networks for natural image matting.” BMVC, 2018.
[7] Jingwei Tang, Yagız Aksoy, Cengiz Oztireli, Markus Gross, Tunc Ozan Aydın. “Learning-based Sampling for Natural Image Matting”, CVPR, 2019.
[8] Feng, Xiaoxue, Xiaohui Liang, and Zili Zhang. “A cluster sampling method for image matting via sparse coding.” ECCV, 2016.
[9] Soumyadip Sengupta, Vivek Jayaram, Brian Curless, Steve Seitz, Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman:
Background Matting: The World is Your Green Screen. CVPR, 2020.
[10] Lu, Erika, et al. “Omnimatte: Associating Objects and Their Effects in Video.” CVPR, 2021.
[11] Zhang, Yunke, et al. “A late fusion cnn for digital matting.” CVPR, 2019.
[12] Hou, Qiqi, and Feng Liu. “Context-aware image matting for simultaneous foreground and alpha estimation.” ICCV. 2019.
[13] Yang, Stephen, et al. “Unified interactive image matting.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.08324 (2022).