Before install guest addition from CD, do the following
sudo apt-get install dkms build-essential linux-headers-generic linux-headers-$(uname -r)For missing linux kernel headers or other common problems, refer to this.
use
uname -roruname -ato look up the kernel version, usedpkg --get-selections | grep linuxto check the installed linux kernels.If you click the sharefolder item in the menubar and get the follwing error: ‘The VirtualBox Guest Additions do not seem to be available on this virtual machine, and shared folders cannot be used without them’, the following commands may be helpful.
1
2
3
4sudo apt-get install virtualbox-guest-additions-iso
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
sudo apt-get install virtualbox-guest-x11
Enlarge VirtualBox vdi
Go to virtualbox installation directory and execute the following command:
D:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage.exe modifyhd "F:\VirtualBox\my ubuntu.vdi" --resize 15360Note 15360 is the new size (M), this command can only enlarge the size.
Install gparted by
sudo apt-get install gpartedand make the extended disk space available to use.Remount
/hometo the new disk. For concrete steps, refer to this link.
Git
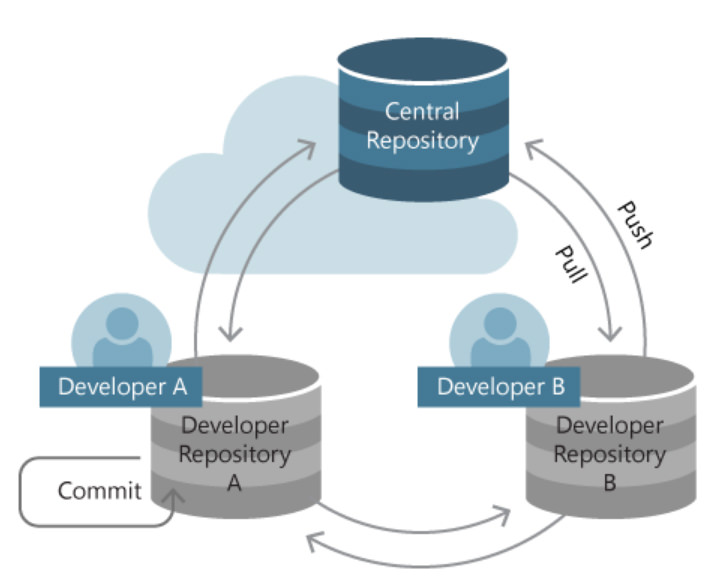
Initialize center and local repository
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11#init from scratch
git init <local_dir>
#for central repository without working directory, use --bare
git init --bare <local_dir>
#clone from GitHub, can just clone a subdirectory. pull all the remote branches. set up "main" branch to track "origin/main".
git clone <remote_repo> <remote_dir>
#pull from other local repository
git remote add <remote_repo> <remote_address>
git pull # only pull the default branch
git pull <remote_repo> <remote_branch> # pull is equal to fetch and merge
git fetch <remote_repo> <remote_branch>Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6git config --global user.name $name
git config --global user.email $email
git config --global credential.helper store
git config --global alias.$alias-name $git-command
git config --system core.editor $editor # e.g., vim
git config --global --edit.git/configRepository-specific settings.~/.gitconfigUser-specific settings. This is where options set with the —global flag are stored./etc/gitconfigSystem-wide settings.Staged snapshot in the staging area
operations on tracked files:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19git add <file>
git add <dir>
git add . # add all the files in the current directory
git add * # add all the files and folders in the current directory
# before using `git add .` or `git add *`, we can exclude the untracked files in `.gitignore` (e.g., `*.<ext>`, `<dir>/`, use `!<file>` for exception).
git rm <file> # delete the file
git rm --cached <file> # untrack the file
git mv <old name> <new name> # mv = rm+add
git restore --staged <file> # move staged changes to unstaged changes
git restore <file> # remove unstaged changes
#clear the entire staging area
git reset HEAD # move all staged changes to unstaged changes
git reset --hard HEAD # remove all staged and unstaged changes
Commit the staged snapshot
1
2
3
4
5git commit -m "<message>" #new commit node
git commit --amend #old commit node
#`-a` means staging all the changes of tracked files
git commit -a -m "<message>"
git commit -a --amendBranch
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8git branch #list local branches
git branch -r # list remote branches
git branch -a # list both remote branches and local branches
git branch -vv # list local branches and their tracked remote branches
git branch -d <old_branch> #use -D enforce delete
git checkout <old_branch> #switch to branch $branch
git branch <new_branch> #create a new branch
git checkout -b <new_branch> #switch to a new branch $branch(a) Imaging there exists a hash table of
key:valuepairs with branch name as key and commit node as value. When checkout a new branch b1,b1:current-commit-codewill be stored in the hash table. When checkout an existing branch b1, you will reach the hashed commit code. In both cases, b1 (HEAD) will be used as the hash key for the next commit node, that is, when you commit next time,b1:new-commit-codewill be updated in the hash table.
(b) Another perspective is treating the branch name as a pointer to the commit node and each branch is a retrospective history dating back from that node, which is essentially the same as (a).When checkout to another branch, git status (staged or unstaged modifications) will be transferred to that branch. If there exists file conflicts (operations on common yet different files), checkout will be forbidden.
Besides
branch, users can also addtagto each commit node.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11#assume the current branch is master
#merge: merge experiment into master
#master moves one step forward, both experiment and original master are its parents
git merge experiment
#assume the current branch is experiment
#rebase: base experiment on master
#duplicate the nodes between C2 and experiment after master, move experiment to up-to-date
git rebase master
#in the simple fast-forward case, assume <branch> is ahead of <branch1>
#then, `merge <branch1> <branch2>` and `rebase <branch1> <branch2>` work the same, just move <branch1> to <branch2>.
#whereas, `merge <branch2> <branch1>` or `rebase <branch2> <branch1>` are not allowed.Tracking changes
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10git status
git log #commit history
git log -n <limit> --stat
git log --all --graph --oneline # show the tree structure of all branches
git log --grep="<pattern>"
git log --author="John Smith" -p hello.py
git diff #view unstaged modification
git diff --cached #view staged modification
git diff <branch1>..<branch2>
git diff <repo>/<branch1>..<branch2>when using
git log, it will only show the ancestral commit nodes of current node.Date back to history
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11#revert the operations in <commit> and add one commit node ahead of HEAD
#revert does not work on file
git revert <commit>
#go back to <commit>
#git checkout <commit> <file> is just copying the <file> in <commit>
git checkout <commit>
#git reset <commit> changes branch name, working directory, and staged index
#git reset <file> is removing the staged file
git reset --mixed <commit> #default, save the working directory
git reset --soft <commit> #save both working directory and staged index
git reset --hard <commit> #save none, dangerous!(a) For reset file, there are no options
--hardand--soft.
(b) For reset commit, afterreset --mixedorreset --hard, there are no staged snapshots. Afterreset --soft, staged snapshots enable the staged index to remain the same. More specifically, at the time before or afterreset --soft, if you rungit commit, the generated commit node should be the same.
Communicate with remote repositories
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9git remote -v #list remote repositories
git remote add <remote_repo> <remote_address>
git branch -r #list the fetched branches of remote repositories
git fetch <repo> # fetch all of the remote branches
git fetch <repo> <remote_branch>:<local_branch>
git checkout -b <new_branch> <repo>/<remote_branch> # Checking out a local copy of specific branch
git pull <repo> <remote_branch>:<local_branch>
git push <origin> <local_branch>:<remote_branch>after merging code to address the conflict, use
git commit -a -m "$message", thengit push.git pullis equal to agit fetchfollowed by agit merge.Clean working directory
1
2
3git clean -f/d #clean untracked files/directory
git clean -f $path #clean untracked files in $path
#`git clean` is often used togther with `git reset —hard`Stashing
If you are working in your repository, and your workflow is interrupted by another project, you can save the current state of your repository (the working directory and the staging index) in the Git stash. When you are ready to start working where you left off, you can restore the stashed repository state. Note that doing a stash gives you a clean working directory, and leaves you at the last commit.
1
2
3
4git stash save # stash the current state
git stash list # see what is in the Git stash:
git stash apply # return your stashed state to the working directory
git stash pop # return your stashed state to the working directory and delete it from the stashNote the commit-tree grows. “git log” prints the path from root to current node. “leave behind” prints the path from current node to the first common ancestor between current node and new node. Detached head will be off any branch, so create a new branch for the detached head.
Tips:
checkoutandresetwork on both file and commit with different meanings and usages, whilerevertonly works on commit.resetis often used for cancelling uncommited changes whilerevertis often used for cancelling commited changes.- Compared with
reset,checkoutandrevertfocus on the modification, so they are forbidden in many cases.
Github User:
- create a repository on GitHub
- create a local folder
git initgit remote add <remote_repo> <remote_address>git pull <remote_repo> <remote_branch>git push --set-upstream <remote_repo> <remote_branch>- add files
git add *git commit -m "msg"git push
Resources:
A good Chinese tutorial for git is here.
A good English tutorial for git is here.
Ubuntu JDK
Remove default OpenJDK
1
sudo apt-get purge openjdk-\*
download jdk(containing jre) and tar.
add into /etc/profile
1
2JAVA_HOME="/home/newly/Program_Files/Java/jdk1.8.0_65"
PATH="$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/jre/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin"set newly installed jdk as default jdk.
1
2
3sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/java" "java" "$JAVA_HOME/bin/java" 1
sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/javac" "javac" "$JAVA_HOME/bin/javac" 1
sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/javaws" "javaws" "$JAVA_HOME/bin/javaws" 1
OpenCV
Locate OpenCV:
1 | pkg-config --modversion opencv //version |
Uninstall OpenCV:
- go to the compile package and
make uninstall - if cannot find the compile package,
sudo find / -name "*opencv*" -exec rm -i {} \;
Install OpenCV:
For Windows: C++(Visual Studio)
- Download latest OpenCV from http://sourceforge.net/projects/opencvlibrary/?source=typ_redirect.
- Make a dir named build. Use cmake to generate OpenCV.sln in build.
- Click OpenCV.sln and CMakeTargets->INSTALL->build. You can build it in both debug and release modes.
- In the environmental variables, add D:\Program Files\OpenCV_3.0.0\build\install\x64\vc11 as OPENCV_DIR, add Path with %OPENCV_DIR%\bin.
- Create a OpenCV project. C/C++->General->Additional Include Directories: $(OPENCV_DIR)\..\..\include
- Linker->General->Additional Library Directories: $(OPENCV_DIR)\lib
- Linker->Input->Additional Dependencies: copy all the lib files. *d.lib means debug mode.
Note that there may be some problems for visual studio to recognize the updated environmental variable. Try to restart the visual studio or recreate the project.
For Linux: install for C++
- pre-install packages
[compiler] sudo apt-get install build-essential
[required] sudo apt-get install cmake git libgtk2.0-dev pkg-config libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev
[optional] sudo apt-get install python-dev python-numpy libtbb2 libtbb-dev libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libtiff-dev libjasper-dev libdc1394-22-dev - download the required version on https://sourceforge.net/projects/opencvlibrary/
- make and install
1
2
3
4
5mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. //cmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE -D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local ..
make
sudo make install
Tips: if you want to install multiple versions of OpenCV, set CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX differently for different versions of OpenCV.
cmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE \
-D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local \
-D INSTALL_PYTHON_EXAMPLES=ON \
-D INSTALL_C_EXAMPLES=ON \
-D OPENCV_EXTRA_MODULES_PATH=../opencv_contrib/modules \
-D PYTHON_EXECUTABLE=/usr/bin/python \
-D BUILD_EXAMPLES=ON ..
If want to turn off some modules, use -D BUILD_opencv_xfeatures2d=OFF
Switch between different versions of OpenCV:
switch from version 3.2 to version 2.4 shell
switch from version 2.4 to version 3.2 shell
For Linux: Python(Anaconda)
source activate tgt_env
conda install -c https://conda.binstar.org/menpo opencv
spyder
Then try import cv2
GStreamer+FFmpeg for Ubuntu14.04
Install gst-plugin
1
2sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ddalex/gstreamer
sudo apt-get install gstreamer0.10-*Install gstffmpeg
1
2
3sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mc3man/gstffmpeg-keep
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gstreamer0.10-ffmpeg
Remote Debugging for Visual Code
Remote-SSH: Open SSH Configuration File ~/.ssh/config
Host jump-box
HostName
User
Port
Host target-box
HostName
User
Port 22
ProxyCommand ssh -q -W %h:%p jump-box
Remote Explorer
Install JDK and Eclipse
For Windows
Download Java JDK from http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html and install. Note that JDK contains JRE. Modify the following environment variables:
- add JAVAHOME D:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jdk1.7.051
- add Path %JAVA_HOME%\bin;\%JAVA_HOME%\jre\bin;
- add CLASSPATH %JAVA_HOME%\lib\tools.jar;%JAVA_HOME%\jre\lib\rt.jar
Download Eclipse from http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/ and click eclipse.exe
For Linux
Install JDK
1
2
3
4sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
sudo apt-get update // depending on the needed java version
sudo apt-get install openjdk-7-jdk
or sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jre openjdk-8-jdkDownload Eclipse and unpack
Create a new file eclipse.desktop in /usr/share/applications/ and add the below code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8[Desktop Entry]
Name=Eclipse
Comment=Eclipse IDE
Exec=/home/liniu/Program_Files/Eclipse/eclipse/eclipse
Icon=/home/ivan/Eclipse/icon.xpm
Categories=Application;Development;Java;IDE
Type=Application
Terminal=0and then run
1
sudo desktop-file-install /usr/share/applications/eclipse.desktop
Add to the path:
sudo ln -s /opt/eclipse/eclipse /usr/local/bin/
Ubuntu MATLAB
- install by running the sh file
- refer to the crack folder
- After installation, create a shortcut
a) sudo ln -s /usr/local/MATLAB/R2012a/bin/matlab /usr/bin/matlab
b) copy the matlab.desktop to /usr/share/applications and matlab.png to /usr/share/icons.
Problem:
/tmp/mathworks……. permission denied
1
2$cd /Matlab.R2012a.UNIX/sys/java/jre/glnxa64/jre/bin
chmod +x ./javawarning: usr/local/MATLAB/R2012a/bin/util/oscheck.sh: /lib/libc.so.6: not found
1
sudo ln -s /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 /lib64/libc.so.6
Medical Image Format
Format
- DICOM: (Digital Imaging and COmmunications in Medicine) meta info + raw data
- nrrd: meta info (e.g., sizes, dimension, encoding, endian) + raw data
The meta info in nrrd mainly consists of the format of raw data while the meta info in DICOM contains the detailed information of patient, study, and series.
There exist matlab and python functions to read DICOM and nrdd files.
- MATLAB
- DICOM: dicominfo, dicomread
- nrrd: nrrdread
- conversion from DICOM to nrrd: Dicom2nrrd
DICOM is generally a directory containing a sequence of slices while nrrd is a single file. The meta info of DICOM is more complicated and thus more error-prone than that of nrrd. Use DICOMPatcher to fix up DICOM files if errors occur when loading them to 3D Slicer.
Software
3D Slicer: cross-platform, compatible with different formats (e.g., DICOM and nrrd), and convert between them.
Other softwares to view medical images: http://www.cabiatl.com/mricro/dicom/#links